What is plant endotherapy?
Plant endotherapy, also known as trunk injection, is a therapeutic method for the application of plant protection treatments to woody plants and palms. This method consists of injecting the plant protection product and/or nutritional substance directly into the vascular system of the plant.
Compared to the traditional aerial treatments, it stands out for the absence of atomisation, pulverisation or spraying of chemical products that contaminate the environment, soils and waters. This method also poses no risk to human and animal health, and it can be used at any time of the day.
For each pest and plant species that will be treated, ENDOterapia Vegetal® applies strict action protocols that ensure the effectiveness of the method and minimise damage to the plant.
After more than 10 years in the ornamental tree treatment sector, the plant endotherapy technique is no longer an alternative system and has become consolidated as a technique for the control of pests and diseases. This technique also has multiple benefits to trees and palms, providing them with a supply of nutrients.
BENEFITS
How does it work?

Plant endotherapy is a treatment that works based on the sap flow capacity inside the plants’ vascular tissue – basically, in the outermost xylem [sapwood or alburnum]. Sap flow is determined by two parameters: respiration and photosynthesis. For this reason, when we have these two variables, the treatment will work at its best. Generally speaking, treatments are almost always carried out in spring and summer, the seasons when there are more pests. However, there are pests, such as the pine processionary, that appear in autumn/winter. In these cases, action needs to be taken in early autumn.
It should be noted that not all trees have the same degree of product permeability; we will have more species that are more porous than others. To solve this problem, we need to treat each species in a unique way, according to its porosity and with a specific pressure, to ensure the perfect penetration of the product without causing mechanical damage to the plant.
Fundamentals
It is extremely important that plant endotherapy treatments (ENDOterapia Vegetal) are carried out by technicians of specialised companies with training in this type of applications of phytosanitary products. This will guarantee the maximum quality of the treatment, ensuring its effectiveness and minimising the damage caused to the plant.
There are several factors that can influence the final outcome of the control of a pathology. Six fundamental factors have been established for the proper control of the pathology. These factors can bee seen in the plant endotherapy hexagon:
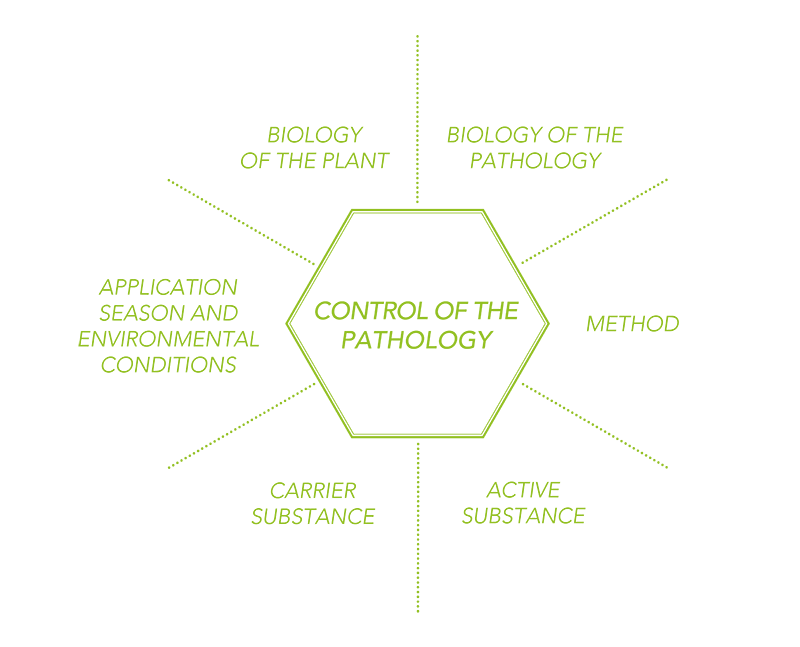
Biology of the plant
First of all, we need to know about the plant to be treated first hand. Therefore, we must differentiate between a tree and a palm tree. A very important feature that distinguishes them is their growth; trees have primary and secondary growth, while palm trees (monocot angiosperms) lack secondary growth.
On the other hand, we need to distinguish between two groups of trees, those belonging to the gymnosperms, which include the group of conifers (pines, firs, cedars, etc.) and those belonging to the dicot angiosperms.
This last group of trees is divided into two subgroups according to the porosity of their wood: diffuse porosity trees (banana, lime tree, poplar, etc.), which have the conductive vessel elements uniformly distributed along the xylem, and annular porosity trees (holm oak, oak, cork oak, catalpa, elm, etc.), which have large vessels in the youngest part of the trunk (in the outermost xylem).
These characteristics will determine the behaviour of the product in the plant’s vascular system and the compartmentalisation or mineralisation of wounds.
Biology of the pathology
Then, we must study the aetiology (the origin) of the pathogen causing the damage. First, we must define whether it is an insect, a microorganism, physiological damage, nutritional deficiency or a combination of more than one of these pathogens. However, a large part of the problems are caused by a type of insect or mite. In this case, we need to properly assess its biological cycle; which family it belongs to, its stage of development and in what season of the year the damage takes place. This way, we will know how, when and with what to carry out the treatment.
In the case of diseases, we must identify the microorganism causing the problem. Most times, this will be a more complicated task than that of identifying an insect, since lab tests are required more than often. Nutritional deficiencies are usually more evident, especially chlorosis due to a lack of iron. However, there are other chlorosis types due to the lack of some other micronutrients. This may also require lab testing to determine which of them is insufficient.
Plant endotherapy plays a fundamental role in IPM (Integrated Pest Management) control strategies for pests, diseases or physiopathies.
Therefore, aetiology responds to how, when and with what product we need to perform the treatment.
Method
The applying technician must know firsthand what system they have in their hands to carry out the treatment. Of course, it must be an equipment approved by the European Union to avoid risks, both for the person who applies it and for the plant and other people.
There are two very important features that must be taken into account to achieve good control without causing damage to the plant:
- The working pressure: the range of pressures can vary depending on the type of wood of the plant to be treated.
- The volume that will be injected: some equipment works with macro-infusion and others with micro-infusion, depending on the volume that will be injected.
Therefore, the more precise the system used in terms of pressure and volume control, the more the error on the part of the person applying it is minimised, and the safer and more efficient the treatment will be.
Active substance
This section, together with the next one, carrier substance, determines the dosage of the treatment, that is, the dosage of the product to be injected. To do so, we need to know the nature of the plant protection product or nutrient. In the case of plant protection product (insecticides and/or fungicides), we need to know the concentration of the active substance, its chemical family and how it acts on the insect or micro-organism.
By using plant endotherapy (ENDOterapia Vegetal), small but highly-concentrated doses of the plant protection product are injected. This is why it is very important to use products that give the maximum possible quality guarantees. There are products with a low active substance percentage, which means that the rest are adjuvants that can significantly modify the qualities of a product or another with the same active substance. This fact that can also affect the final result of the treatment.
Knowing the chemical family and the mode of action is also important. We need to know if they act either by affecting the nervous system, such as neonicotinoids (agonists of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor) or by affecting the nervous and the muscular system, such as avermectins (chloride channel activators).
In the case of nutrients, their content of macro and micronutrients is also very decisive, since an excess of some of them can cause phytotoxicity.
Carrier substance
Carrier substance or emulsifier is understood as the product that stabilises an emulsion with a plant protection product so that it properly spreads inside the plant, favouring its distribution and persistence.
Its function is to balance pH, electrical conductivity and density, in addition to achieving a completely homogeneous mixture over time. This avoids the precipitation of the active substance or any other component of the plant protection product.
Precipitation can cause phytotoxicity problems due to an excess of concentration of the plant protection product. The precipitate can collapse the conductive vessel elements and consequently cause the non-translocation of the product in the whole plant.
Application season and environmental conditions
Because plant endotherapy is a technique that works through the sap flow of the plant, which is determined by respiration and photosynthesis, the application season and the climatic and environmental conditions will be very important for these two factors to be fully operational.
The season of application should coincide with the time of active growth of the plant, which is the period of maximum sap flow. Transpiration through the leaves creates a negative pressure in the xylem (less than 1 atm), which allows the “raw sap” to flow upward. The raw sap transports water, minerals and other elements in solution, such as the injected product.
Climatic conditions intervene in the transpiration process. Therefore, having optimum light, warm temperatures and relative humidity is very important. These factors affect the opening of the stomata, which are the main actors in charge of plant transpiration. Solar energy causes an increase in temperature that accelerates the transpiration rate. A high relative humidity causes slower water loss because the air is saturated with water vapour and the plant closes its stomata. Wind also has an influence on this process. It increases the gradient of water vapour concentration between the inside of the leaf and the surrounding air, dragging the water vapour from the leaf surface.
Light and temperature are also decisive for the photosynthetic process in which the plant elaborates its food. It transforms raw sap into sap made from atmospheric CO2 (carbon dioxide), water and minerals with the help of sunlight. The sap it makes mainly contains sugars, besides water, plant growth regulators and dissolved minerals. It is transported by the phloem from the leaves and the green stems to the roots, passing through the whole plant.
Injection methodology
Drilling

First, the perimeter of the trunk is drilled approximately every 30-40 cm.
Placement
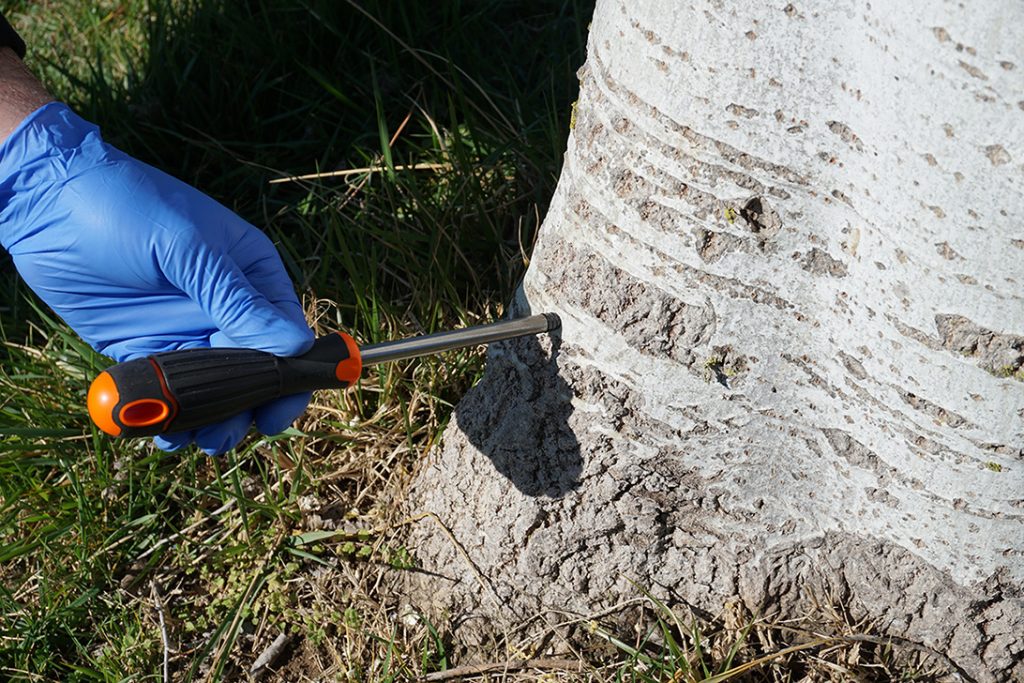

The ENDOplug is then placed in the hole. This is a catheter that the injection needle will go through, allowing the product to go in and preventing it from leaking out.
Adjustment
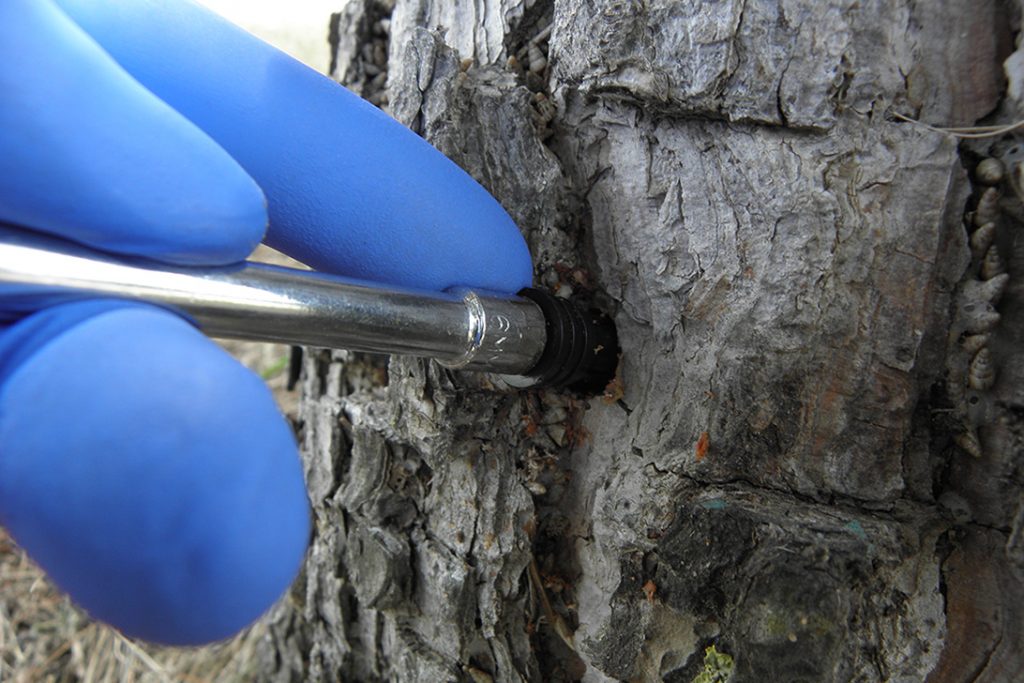

Using a nylon hammer and a special positioner, the ENDOplug is fixed into the hole made in the tree.
Injection
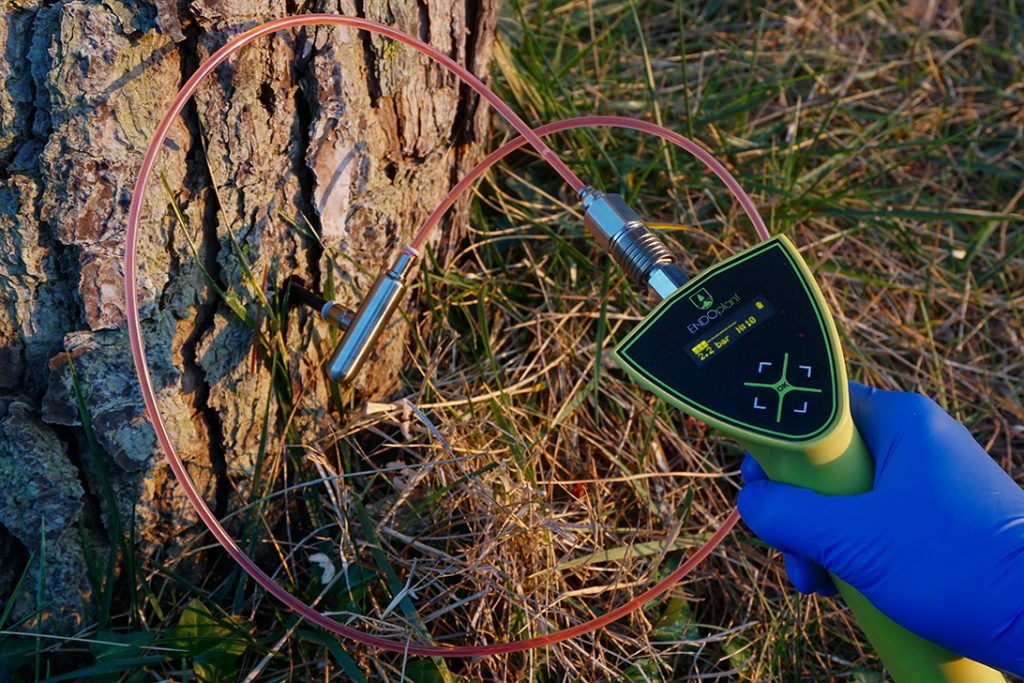

Finally, the injection is performed with the selected trunk injection mechanism, inserting the needle into the ENDOplug.

